목록수학(Mathematics) (10)
미국 고딩의 물리학노트
The ultimate goal of calculus is deriving the derivative and antiderivative of a given function. If so, what is the concept in multivariable calculus corresponding with "derivatives"? Yet we cannot propose a perfectly matching concept, by iterating the actual process of getting the derivative fixed on a certain plain. We call this concept a partial derivative. Partial derivative is the derivativ..
미적분학의 궁극적인 목표는 함수의 도함수와 역도함수를 구하는 것이다. 그렇다면 다변수함수의 "도함수"에 해당하는 개념은 무엇일까? 비록 그것을 바로 구할 수는 없으나, 우리는 편미분이라는 일변수함수의 도함수와 상당히 유사한 개념을 도입하여 그 힌트를 얻을 수 있다. (편미분 자체가 훌륭한 수학적 도구이기도 하다.) 편미분은 n변수함수의 특정 변수를 제외한 나머지 변수를 상수로 간주하여 미분하는 것이다. $n$변수함수 $f$에 대해서, 점 $\left ( a_{1},a_{2},...,a_{n} \right )$에서 변수 $x_{i}$에 관한 $f$의 편미분계수는 다음과 같은 극한이다. $$\frac{\partial f}{\partial x_{i}}\left ( a \right )=\lim_{\Delta x..
Defining limits using epsilon-delta proof of a multivariable function takes more logical challenges than a single-variable function. However, the overall structure of the definition is not different from the definition of limit of a single-variable function. When $n=1$, the definition below is identical to the single-variable one. A function $f:\mathbb{R}^{n}\rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ is defined in..
다변수함수에 엡실론-델타 논법을 적용시키는 것은 일변수함수의 그것보다 약간의 논리적 도약을 요구한다. 사실, 전체적인 정의의 구조는 일변수함수의 엡실론-델타 논법과 전혀 다르지 않다. $n=1$인 상황에서 아래 정의는 일변수함수의 극한의 정의와 완벽하게 일치한다. $n$변수실함수 $f$가 중심이 $\left ( c_{1},c_{2},...,c_{n} \right )$인 $n$차원 초구에서 정의된다고 하자. 이때 $$\lim_{(x_{1},...,x_{n})\rightarrow (c_{1},...,c_{n})}f(x_{1},x_{2},...,x_{n})=L$$이란 임의의 $\varepsilon >0$에 대하여 적절한 $\delta >0$가 존재하여 $$0
To be short, the multivariable function is a function that depends on several arguments. A real function with n variables has a domain as a subset of $\mathbb{R}^{n}$, a range as a subset of $\mathbb{R}$. On 3-dimensional cartesian coordinates, the domain is a subset of xy plane and the range is a subset of all real numbers on z axis. Similary, the graph of real function with n variables f is a ..
간단히 말해서, 독립변수가 둘 이상인 함수를 다변수함수라 한다. n변수실함수는 정의역이 $\mathbb{R}^{n}$의 부분집합이고, 치역이 $\mathbb{R}$의 부분집합이다. 3차원 직교좌표계 위에서, 정의역은 xy평면의 부분집합으로 표현되고, 치역은 z축으로 표시된 실직선 위 수들의 집합이다. 비슷하게, n변수실함수 f의 그래프는 $(x_{1},x_{2},...,x_{n})$가 정의역 D에 속하고 $y=f(x_{1},x_{2},...,x_{n})$인 $\mathbb{R}^{n}$에 속하는 점 $(x_{1},x_{2},...,x_{n},f)$ 전체의 집합이다. $\mathbb{R}^{n}$의 점 $(x_{1},x_{2},...,x_{n},f)$과 위치벡터 $\mathbf{x}=\left \langl..
For the sake of convenience, Vector is defined as a quantity with both magnitude and direction. In contrast, a quantity with a magnitude but no direction is defined as Scalar. Mathematically, the vector is an element defined inside a vector space. Details would be discussed in linear algebra, so it is rather convenient to think of a set of every existing vector on 3-dimensional space. This set h..
계산의 편리함을 위해, 벡터는 당분간 크기와 방향을 지닌 양으로 정의한다. 이와 반대되게 크기만을 가진 값을 스칼라라고 한다. 수학적으로, 벡터는 벡터 공간에서 정의되는 원소이다. 자세한 것은 선형대수에서 다루겠지만, 현재로썬 3차원 공간 상에서 존재하는 모든 벡터의 집합을 생각하는 것이 편리하다. 이 벡터의 집합에 대해 우리가 중요하게 알아야 할 두 가지 성질이 있다. 1. 덧셈이 정의된다. 벡터의 덧셈은 교환법칙과 결합법칙이 성립하며, 덧셈의 항등원이 존재한다. $$\mathbf{A}+\mathbf{B}=\mathbf{B}+\mathbf{A}$$ $$(\mathbf{A}+\mathbf{B})+\mathbf{C}=\mathbf{A}+(\mathbf{B}+\mathbf{C})$$ $$\mathbf{A}+..
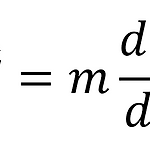 Relationship between Physics and Mathematics
Relationship between Physics and Mathematics
Physics has an inseparable relationship with mathematics. There are many ways to describe the laws of the world. At one time, almost everyone tried to explain the world's logic by affirming the existence of the absolute or God. Philosophers tried to explain the structure of the world through logic and reasoning, or through anticipation and imagination. Numerous poets and writers have demonstrate..
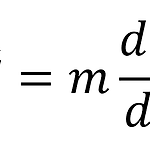 물리학과 수학은 어떤 관계에 있는가?
물리학과 수학은 어떤 관계에 있는가?
물리학은 수학과 뗄레야 뗄 수 없는 관계를 가지고 있다. 그 역은 대체로 성립하지 않는다. 이 세상의 법칙을 기술하는 데는 여러가지 방법이 있다. 한때 거의 모든 사람은 절대자 또는 신의 존재를 긍정함으로써 세상의 이치를 설명하려 했다. 철학자들은 논리와 추론, 혹은 예상과 상상을 통해 세상의 구조를 설명했다. 수많은 시인들과 작가들은 상상의 나래를 펼치며 세상의 아름다움과 추함을 대중에게 설명했다. 그러나 우리 모두가 긍정할 수 있는 한 가지가 있다면, 바로 인간의 감각은 세상을 설명하는 데는 너무나도 부정확하다는 것이다. 우리의 오감은 너무나도 쉽게 바뀌며, 감각이 쌓는 우리의 기억 역시 완벽하지 않다. 개인마다 생길 수 밖에 없는 오차는 결국 종교전쟁, 지식계층의 박해, 그리고 이성에 대한 무관심을..
